Lesson 5: Narrow Complex Tachycardia 2
- Tooba Alwani
- Feb 27
- 2 min read
Updated: Mar 27
Summary of Learning Points
“Irregularly Irregular” Rhythms
Include Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter with variable conduction
Variable R-R interval with no discernible repeating pattern of variation
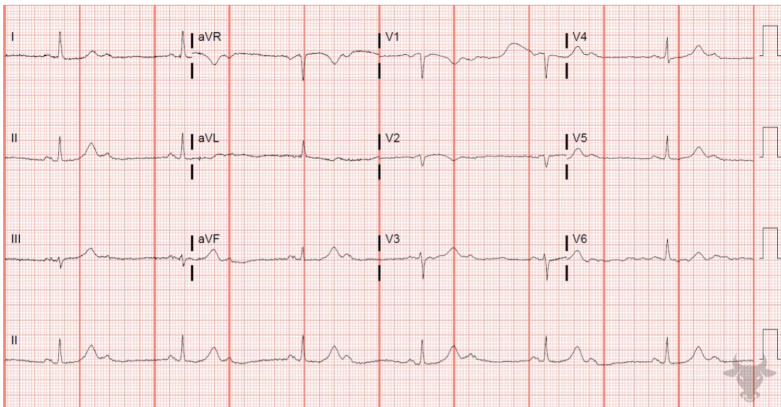
Atrial Fibrillation
A disorganized and chaotic atrial rhythm that leads to erratic atrial contraction with impulses intermittently conducted through to the ventricles
The exact underlying electrophysiology is uncertain, though theories have been proposed including ectopic origins of aberrant rhythms in the pulmonary veins leading to “atrial R on T”
Larger LA leads to increased space for wandering/reentrant circuits which can lead to higher risk of developing and maintaining atrial fibrillation
ECG Key Characteristics: Absent P-Waves, Irregularly Irregular R-R Interval, may see fibrillatory waves
Differentiate coarse fibrillatory waves from P-Waves by comparing old ECG’s
Atrial Flutter
An organized atrial arrhythmia characterized by a macro-reentrant circuit usually located around the CTI
Classified into typical and atypical, with important treatment implications between the two
Typical Flutter: Located around the Cavotricuspid Isthmus, usually in a counterclockwise direction
Atypical Flutter: Macro-reentrant circuit elsewhere in the atria, usually associated with prior procedure/structural derangements
ECG Findings: Atrial rate ~300 bpm (quite specific for flutter), most commonly inverted flutter waves in inferior leads and upright in V1, atrial rate is typically divisible by ventricular rate based on conduction ratio (2:1, 3:1, 4:1 = 150, 100, 75)
Treatment Implications
Atrial fibrillation is easier to medically rate control given micro-reentrant circuits +/- wandering ectopic wavelets
Atrial flutter is often harder to medically rate control due to presence of macro-reentrant circuit
Atrial flutter can be easier to ablate/cure, with typical flutter usually accessible to ablation at the CTI.
Atypical flutter can be more challenging to ablate/cure given variable location, may require more complex techniques such as ethanol ablation or crossing the septum into the LA.
Practice ECG
Answer